√1000以上 s p d f orbitals 164053-S p d f orbitals diagram
S orbital electrons will have a lesser amount of energy (more negative) than that of p orbital electrons which will have lesser energy than that of d orbital electrons As the extent of shielding from the nucleus is different for electrons in different orbitals, it leads to the splitting of energy levels having the same principal quantum numberHow many electrons do the F orbitals holds total?Elements in the long form of periodic table have been divided into four blocks ie s ,p ,d and f This division is based upon the name of the orbitals which receives the last electron S block elements 1)Elements in which the last electron enters the s orbital of their respective outermost shells are called

Spdf Orbitals Location Diagram Quizlet
S p d f orbitals diagram
S p d f orbitals diagram-Elements in the long form of periodic table have been divided into four blocks ie s ,p ,d and f This division is based upon the name of the orbitals which receives the last electron S block elements 1)Elements in which the last electron enters the s orbital of their respective outermost shells are calledPrincipal shell 4n has s, p, d, and f orbitals and can hold 32 electrons Moving away from the nucleus, the number of electrons and orbitals found in the energy levels increases Progressing from one atom to the next in the periodic table, the electron structure can be worked out by fitting an extra electron into the next available orbital



What Is Spdf Configuration Chemistry Stack Exchange
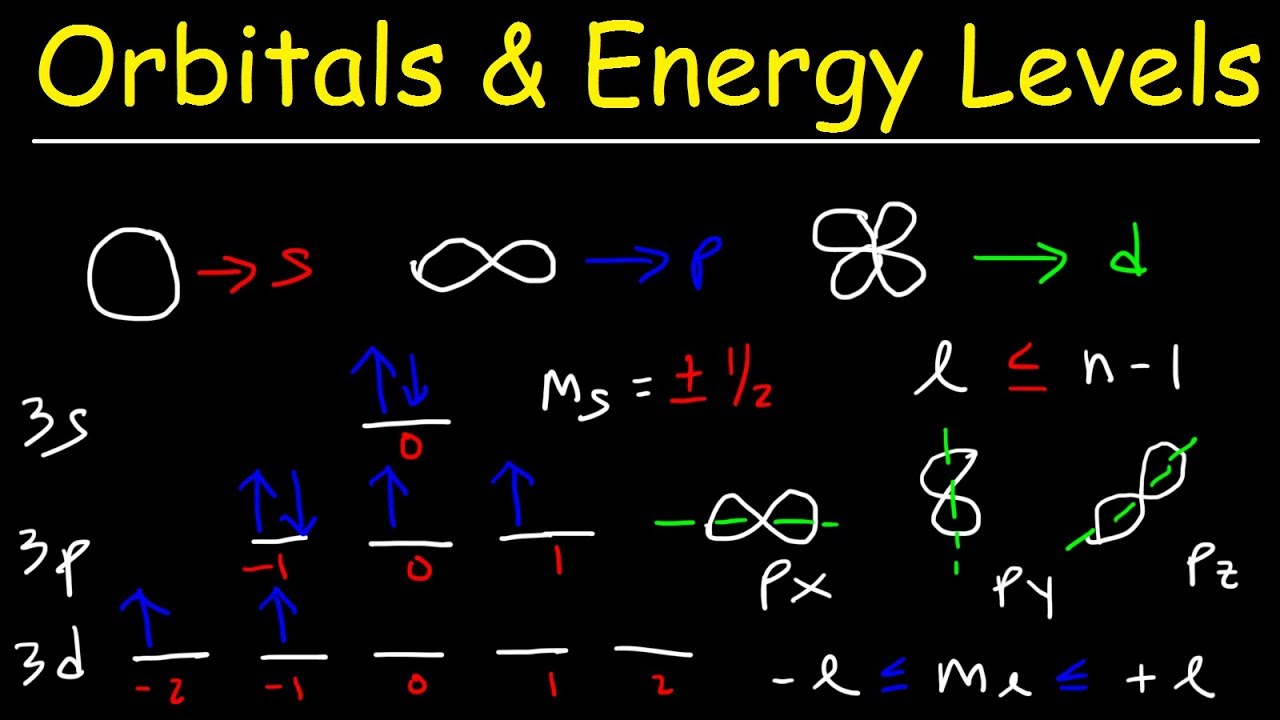
This number divides the subshell into individual orbitals which hold the electrons;Is there any order in filling the orbitals?18 orbital quantum number identifies the type of orbital S 0 P 1 D 2 F 3 Ml magnetic quantum number S O P 1 O O O 1 D 2 O O O O O 2 F 3 O O O O O O O 3 Ms spin quantum number Ø = 1/2 ⨂ = 1/2 S
The order of the amount of shielding done is also in the order s, p, d, f Since the 2s electron has more density near the nucleus of an atom than a 2p electron, it is said to shield the 2p electron from the full effective charge of the nucleus32 how many total electrons does the 4th energy level hold?How many electrons do the F orbitals holds total?
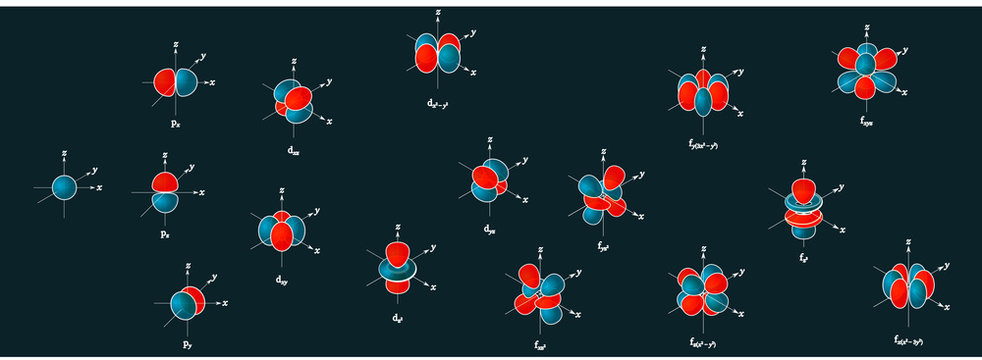
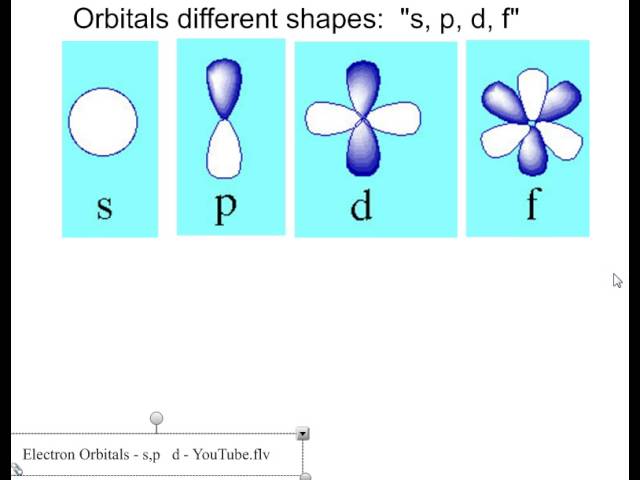
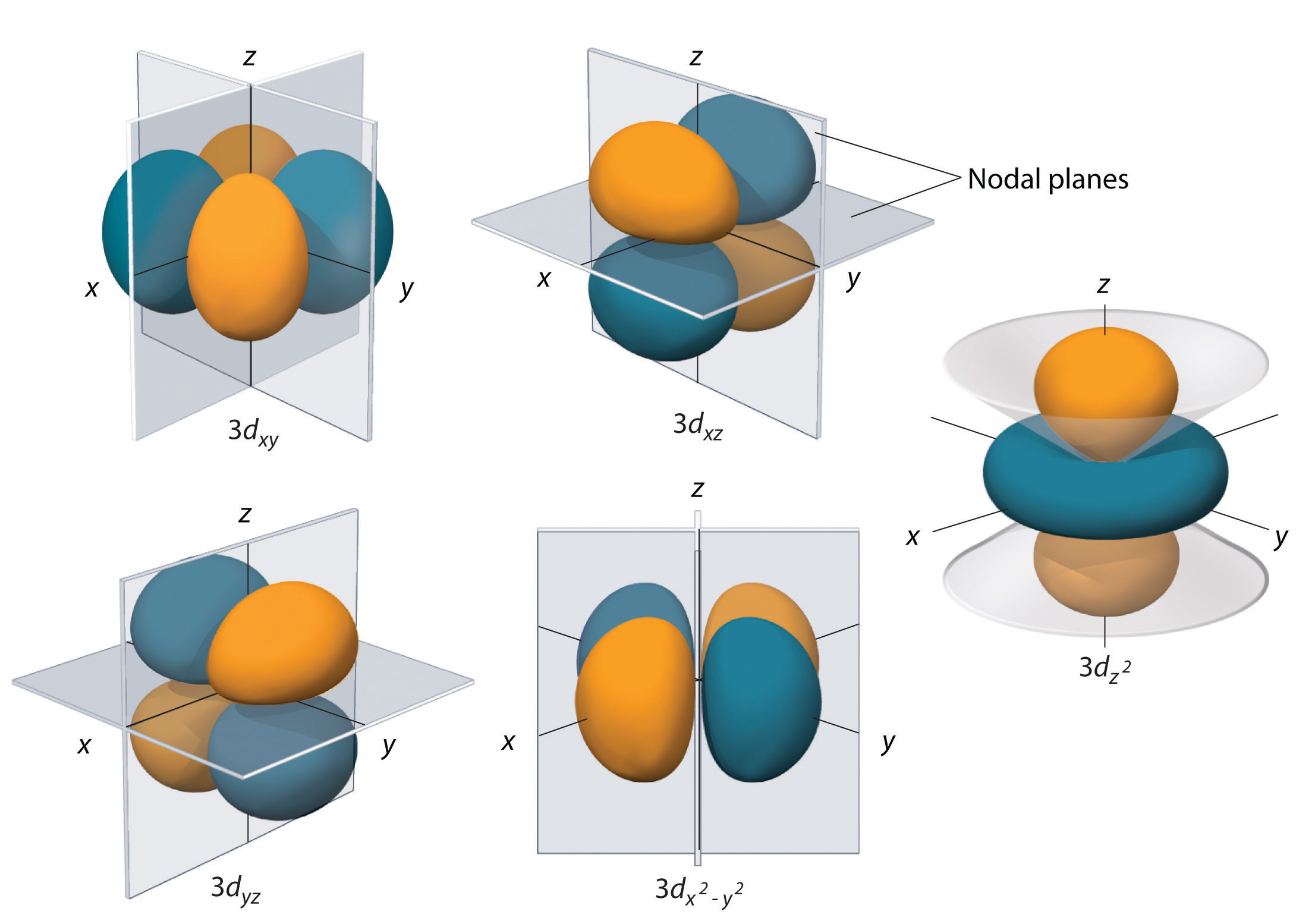
Porbitals are orientated in three different directions along X, Y and Z axis of the usual coordinate system These orbitals are designated as P x, P y & P z orbitals porbital have one nodal plane d – orbital For d orbital Azimuthal quantum number l = 2 and the magnetic quantum number m = 2, 1, 0, 1, 2 Hence d orbitals have fiveD and f orbitals In addition to s and p orbitals, there are two other sets of orbitals which become available for electrons to inhabit at higher energy levels At the third level, there is a set of five d orbitals (with complicated shapes and names) as well as the 3s and 3p orbitals (3p x, 3p y, 3p z) At the third level there are a total ofThis video explains s, p, d, and f orbitals, sublevels, and their shapes It discusses the 4 quantum numbers n, l, ml, and ms n represents the energy leve


D Orbital Stock Photos And Royalty Free Images Vectors And Illustrations Adobe Stock



Parsing The Spdf Electron Orbital Model Chemistry Education Chemistry Classroom Teaching Chemistry
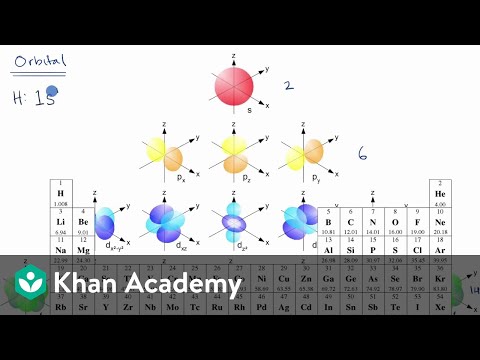
Now, you'll also hear the term, subshell, subshell, or sometimes people will say sublevels and that's where they're talking about s or p or d and eventually f so if I circle this, I'm talking about that first shell Now, the first shell only contains one subshell and that's the 1s subshell and the 1s subshell only has one orbitalUsing s p d f notations decribe the orbital with following quantum no 1 n 2 l 1 2 n 4 l 0 3 n 5 l 3 4 n 3 l 2 db3oo Chemistry TopperLearningcomThe simple names s orbital, p orbital, d orbital, and f orbital refer to orbitals with angular momentum quantum number ℓ = 0, 1, 2, and 3 respectively These names, together with the value of n , are used to describe the electron configurations of atoms


Parsing The Spdf Electron Orbital Model


How To Use Spdf Method For Electronic Configuration Chemistry Topperlearning Com 8ekub122
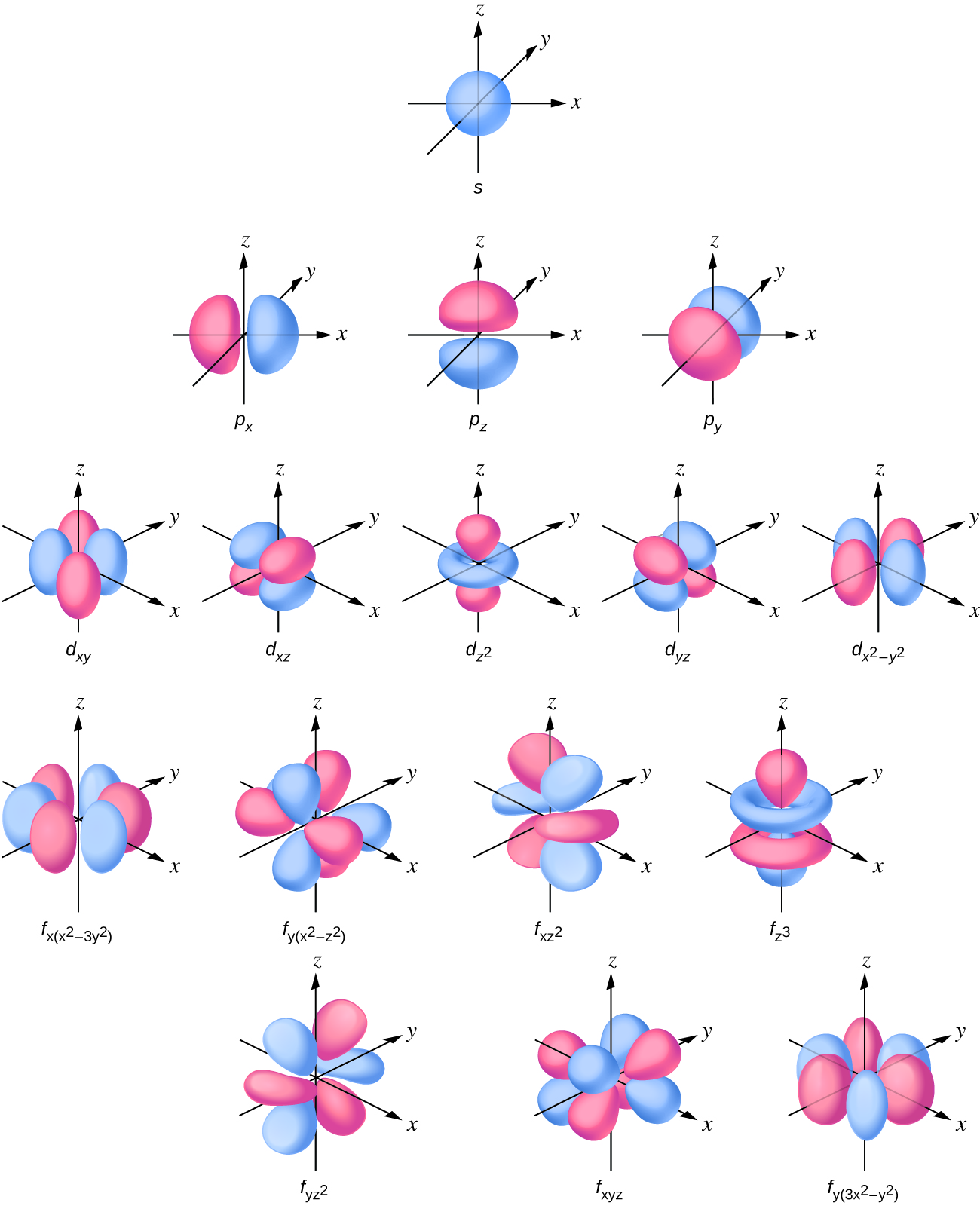
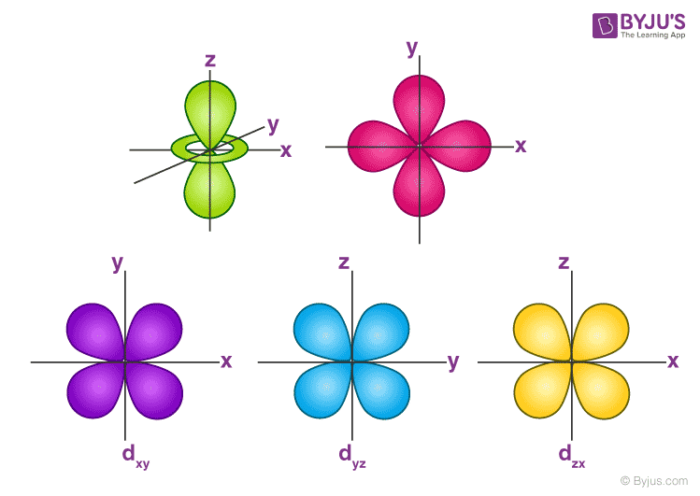
I know there are orbitals named S, P, D and F But why they named like that is there any significance for the letter?An illustration of the shape of the 3d orbitals Click the images to see the various 3d orbitals There are a total of five d orbitals and each orbital can hold two electrons The transition metal series is defined by the progressive filling of the 3d orbitalsThese five orbitals have the following m l values m l =0, ±1, ±2,Fred Senese of Antoine Frostburg explains "You might expect that the 's' stands for 'spherical' and 'p' stands for 'polar' because these imply the shapes of the s and p orbitals, but unfortunately, the letter designations have nothing to do with


Shapes Of Orbitals S P D Shapes


Electron Configurations Orbitals Energy Levels And Ionisation Energy Trends A Level Chemistry Revision Notes
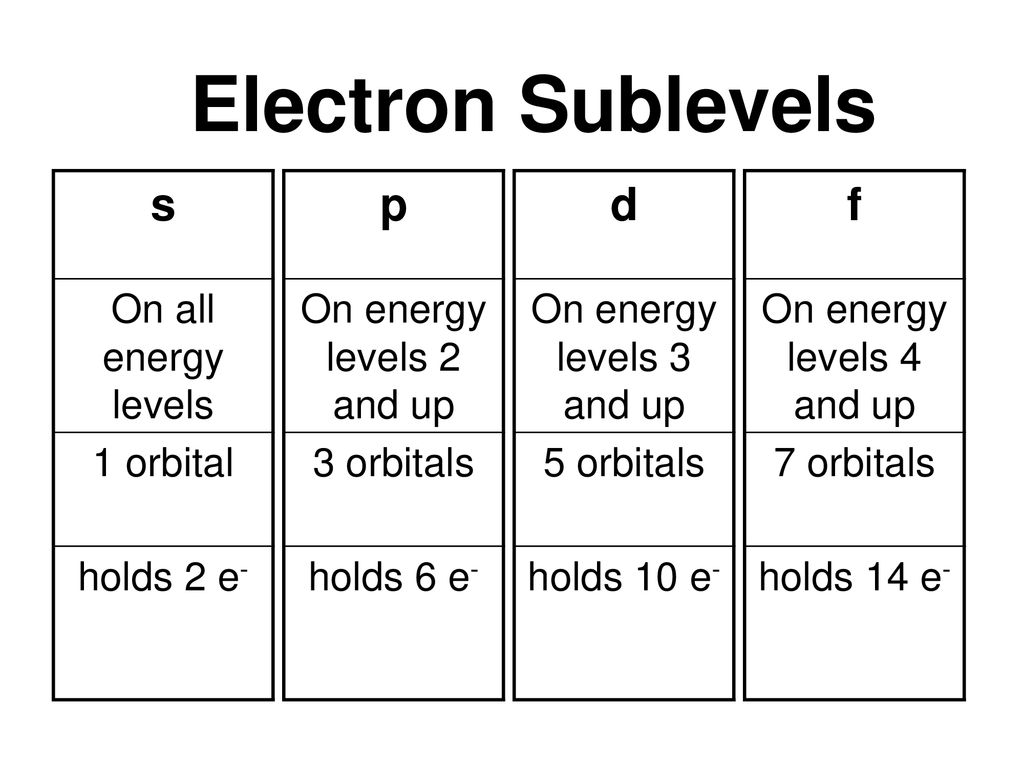
2) Orbitals are combined when bonds form between atoms in a molecule There are four types of orbitals that you should be familiar with s, p, d and f (sharp, principle, diffuse and fundamental) Within each shell of an atom there are some combinations of orbitalsA s orbital _ 2__ b the subshell of p orbitals __ 6___ c the subshell of d orbitals _ 10 __ d the subshell of f orbitals__ 14 __ e the subshell of g orbitals__ 18 __ 10 How many electrons can inhabit all of the n=4 orbitals?Orbital Shapes (s, p, d and f) Explanation The proposed tetrahedral nucleus structure , along with rules for proton spin alignment that is the cause of the repelling force used to calculate orbital distances , can explain the shapes of the s, p, d and f orbitals


Electron Configurations How To Write Out The S P D F Electronic Arrangements Of Atoms Ions Periodic Table Oxidation States Using Orbital Notation Gce A Level Revision Notes



Orbitals Diagram For Spdf Quantum Numbers In High School Chemistry Physics And Mathematics Chemistry Classroom Teaching Chemistry
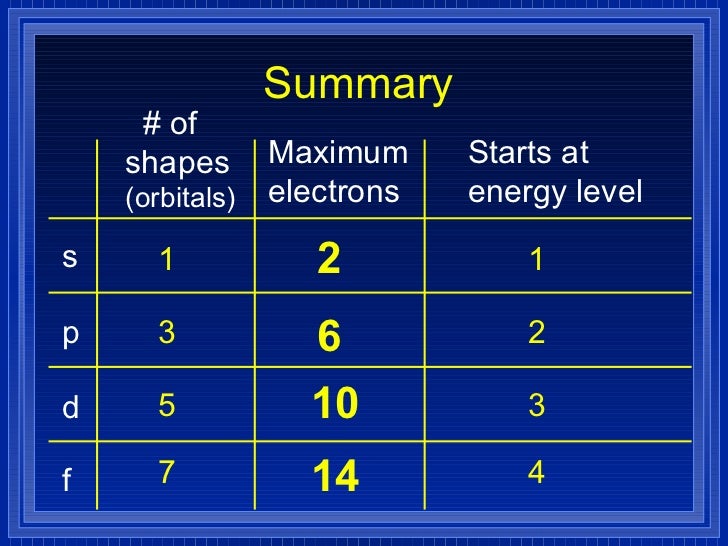
Letter s p d f g h The subshell with n=2 and l=1 is the 2p subshell;Each of these subshells (s, p, d and f) can hold specific maximum numbers of electrons s = 2, p = 6, d = 10, and f = 14 These subshells are further divided into orbitalsThe filling up electronic orbitals with electron around the nucleus of atoms takes place according to the certain configuration formulas, the maximum number of electrons in the main quantum shell = 2n 2, where n = principal quantum number The maximum number of the electron in subshell like s, p, d, and f orbitals = 2(2l1)



File Atomic Orbitals Spdf M Eigenstates Mpositive Png Wikimedia Commons



What Is Spdf Configuration Chemistry Stack Exchange
D and f orbitals In addition to s and p orbitals, there are two other sets of orbitals which become available for electrons to inhabit at higher energy levels At the third level, there is a set of five d orbitals (with complicated shapes and names) as well as the 3s and 3p orbitals (3p x, 3p y, 3p z) At the third level there are a total ofS, p, d, f and so on are the names given to the orbitals that hold the electrons in atoms These orbitals have different shapes (eg electron density distributions in space) and energies (eg 1s is lower energy than 2s which is lower energy than 3s;These are s, p, d and f The shapes of these orbitals are discussed below sorbitals The sorbitals are solid spherical shape around the nucleus When principal quantum number n = 1 and azimuthal quantum number l = 0, that is 1s orbital which is closest to the nucleus When n = 2 and l = 0 , ie 2s orbital which contains one node



File Atomic Orbitals Spdf M Eigenstates And Superpositions Png Wikimedia Commons


S P D F Orbitals Chemistry Socratic
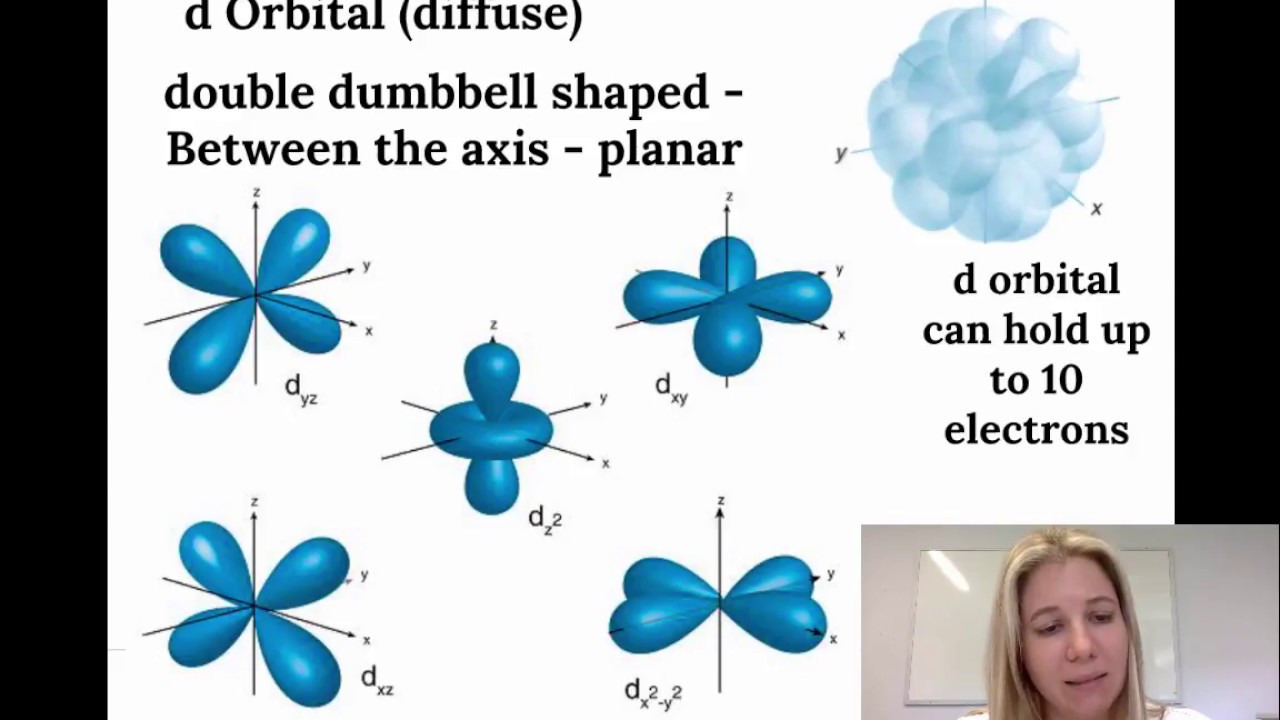
4s = 2 4p = 6 4d = 10 4f = 14 32 Total ElectronsThere are 2l1 orbitals in each subshell Thus the s subshell has only one orbital, the p subshell has three orbitals, and so on Spin Quantum Number (m s) m s = ½ or ½ Specifies the orientation of the spin axis of an electronThere are four different kinds of orbitals, denoted s, p, d and f each with a different shape Of the four, s and p orbitals are considered because these orbitals are the most common in organic and biological chemistry An sorbital is spherical with the nucleus at its centre, a porbitals is dumbbellshaped and four of the five d orbitals are cloverleaf shaped


Chapter 5 Electrons In Atoms


Electron Configurations How To Write Out The S P D F Electronic Arrangements Of Atoms Ions Periodic Table Oxidation States Using Orbital Notation Gce A Level Revision Notes
The overlap situation becomes extreme when the forbitals are added to the s/p/d sum The general forbital set is used in the figure Of note is the change in the number of lobes required to accommodate a pair of electrons 1 for 2, 7 for 8, 25 for 18, and ~64 for 32 along with a few toriS, p, d and f orbitals are possible 6 Which one of the following statements is correct?32 how many total electrons does the 4th energy level hold?



What Is Spdf Configuration Chemistry Stack Exchange



Ppt S P D F Orbitals Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
2s is lower energy than 2p)(image source)So for example,S orbital electrons will have a lesser amount of energy (more negative) than that of p orbital electrons which will have lesser energy than that of d orbital electrons As the extent of shielding from the nucleus is different for electrons in different orbitals, it leads to the splitting of energy levels having the same principal quantum numberAtomic orbitals s, p, d, and f The s orbital is spherical in shape;
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/antibonding-5b54ef9046e0fb005b6d11a9.jpg)


S P D F Orbitals And Angular Momentum Quantum Numbers


Quantum Model And Spdf Orbitals Youtube
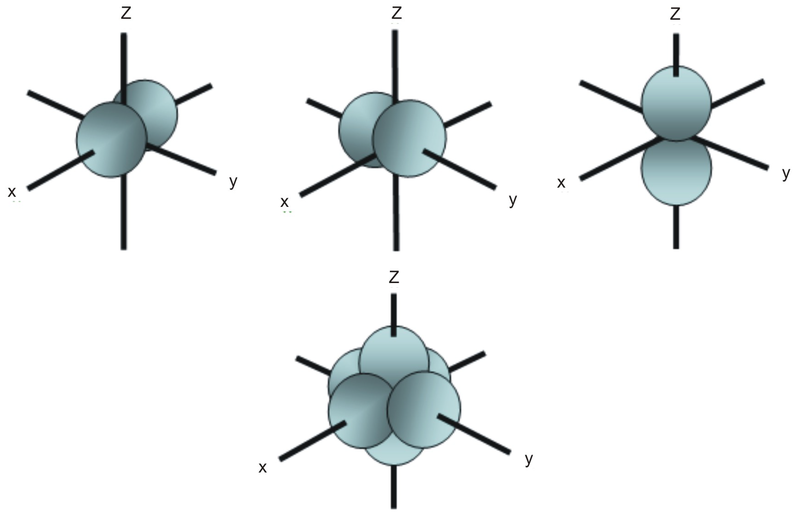
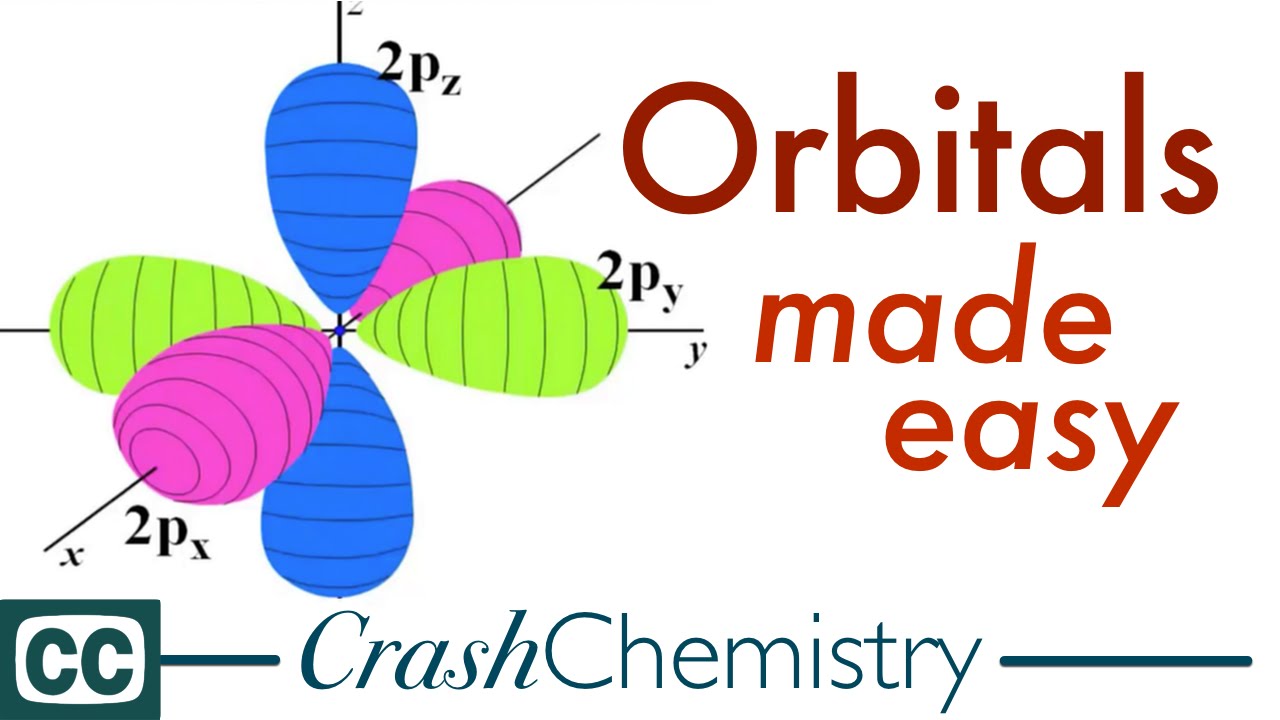
The nucleus resides at the center of the sphere It does not orient itself in any direction In other words, it is nondirectional There are three dumbbellshaped p orbitals Each orbital has two lobes aligned in one of the three axesIf n=3 and l=0, it is the 3s subshell, and so Thus the s subshell has only one orbital, the p subshell has three orbitals, and so on 4 Spin Quantum Number (m s) m s = ½ or ½ Specifies the orientation of the spin axis of an electron An electron can spin inS2 p6 d10 f14 All these orbitals can hold that many electrons, but it is possible to have a partially filled orbital ie 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p3 The last orbital can hold up to 6 e but only holds 3 for this atom, which would be Phosphorus


Q Tbn And9gcth1rc3hbnde1titk095wzz5fdzyo5obndscg8azgis25 Lq4re Usqp Cau



Orbitals And Placing Electrons To Orbitals With Examples Online Chemistry Tutorials
Atomic Orbitals A Electron Location • Sublevel –Shape of electron cloud • s = spherical • p = dumbbell • d = too complex • f = too complex • 1st E level has 1 sublevel s • 2nd E level has 2 sublevels s and p • 3rd E level has 3 sublevels s, p, and d • 4th E level has 4 sublevels s, p, d and f2s is lower energy than 2p)(image source)So for example,S, p, d, f and so on are the names given to the orbitals that hold the electrons in atoms These orbitals have different shapes (eg electron density distributions in space) and energies (eg 1s is lower energy than 2s which is lower energy than 3s;



Orbitals Chemistry For Non Majors


Parsing The Spdf Electron Orbital Model
The orbital shapes are s, p, d, and f Summarize Aufbau's rule for filling orbitals P orbitals have 3 different rotations along the x y and z axes Summarize Hund's rule for filling orbitals Electrons Share When filling similar orbitals, distribute one electron2s is lower energy than 2p)(image source)So for example,S Orbital Versus P Orbital While orbital numbers (eg, n = 1, 2, 3) indicate the energy level of an electron, the letters (s, p, d, f) describe the orbital shape The s orbital is a sphere around the atomic nucleus Within the sphere there are shells in which an electron is more likely to be found at any given time The smallest sphere is 1s


Q Tbn And9gcth1rc3hbnde1titk095wzz5fdzyo5obndscg8azgis25 Lq4re Usqp Cau


What Is The Structure Of An F Orbital Quora
No p orbitals exist in the first energy level, but there is a set of three in each of the higher levels These triplets are oriented in space as if they were on three axes at right angles to each other and may be distinguished by subscripts, for example, 2p x, 2p y, 2p zIn all but the first two principal levels, there is a set of five d orbitals and, in all but the first three principalThe magnetic quantum number is the third on the list between spin and azimuthal quantum number It splits the subshells ( such as s,p,d,f) into individual orbitals and places the electron in one of them It defines the orientation in space of a given orbital of a particular energy (n) and shape (I)S, p, d, f and so on are the names given to the orbitals that hold the electrons in atoms These orbitals have different shapes (eg electron density distributions in space) and energies (eg 1s is lower energy than 2s which is lower energy than 3s;



Quantum Numbers N L Ml Ms Spdf Orbitals Youtube


Electron Configurations
Orbitals Share Improve this question Follow asked Jul 19 '16 at 1008 Kazhian Kazhian 111 1 1 silver badge 5 5 bronze badgesThe orbital shapes are s, p, d, and f Summarize Aufbau's rule for filling orbitals P orbitals have 3 different rotations along the x y and z axes Summarize Hund's rule for filling orbitals Electrons Share When filling similar orbitals, distribute one electronS2 p6 d10 f14 All these orbitals can hold that many electrons, but it is possible to have a partially filled orbital ie 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p3 The last orbital can hold up to 6 e but only holds 3 for this atom, which would be Phosphorus


Introduction To Electron Configurations Video Khan Academy


Parsing The Spdf Electron Orbital Model
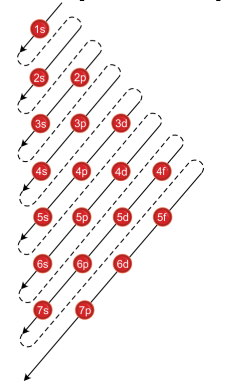
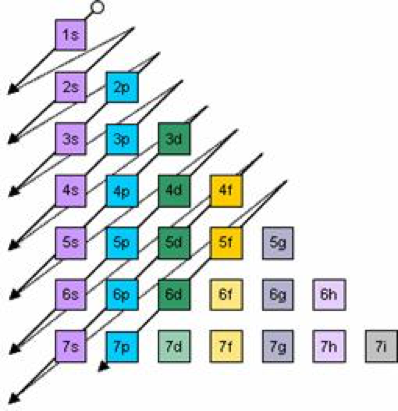
The letters s, p, d, and f were assigned for historical reasons that need not concern us All we have to do is remember the shapes that correspond to each letter Since an electron can theoretically occupy all space, it is impossible to draw an orbital All we can do is draw a shape that will include the electron most of the time, say 95% of the time We call this shape the 95% contour s ORBITALSThe s orbital, p orbital, d orbital, and f orbital refer to orbitals that have an angular momentum quantum number ℓ = 0, 1, 2, and 3, respectively The letters s, p, d, and f come from the descriptions of alkali metal spectroscopy lines as appearing sharp, principal, diffuse, or fundamentalBecause the order of electron penetration from greatest to least is s, p, d, f;


Parsing The Spdf Electron Orbital Model
/800px-Orbital_representation_diagram.svg-589bd6285f9b58819cfd8460.png)


Electron Configuration Chart
According to Hund's rule, when electrons occupy orbitals of equal energy, one electron enters each orbit until_____ a) all the orbitals contain one electron, with spins parallel b) all the orbitals contain one electron, with opposite spins c) there are two electrons in each orbitals d) electron velocities become constantThe main difference between s orbital and p orbital is that s orbitals are spherical shaped whereas p orbitals are dumbbell shaped References 1 Libretexts "Atomic Orbitals" Chemistry LibreTexts, Libretexts, 3 Nov 15, Available here Accessed 31 Aug 17 2 Helmenstine, PhD Anne Marie "What Is a P Orbital?" ThoughtCoD and f orbitals In addition to s and p orbitals, there are two other sets of orbitals that become available for electrons to inhabit at higher energy levels At the third level, there is a set of five d orbitals (with complicated shapes and names) as well as the 3s and 3p orbitals (3p x, 3p y, 3p z) At the third level there are nine total



Electron Configuration Electron Configuration Flashcards Quizlet


2 2 Atomic Orbitals And Quantum Numbers Chemistry Libretexts
18 orbital quantum number identifies the type of orbital S 0 P 1 D 2 F 3 Ml magnetic quantum number S O P 1 O O O 1 D 2 O O O O O 2 F 3 O O O O O O O 3 Ms spin quantum number Ø = 1/2 ⨂ = 1/2 SThe 3d sub level is filled before the 4s sub level the 3rd principal energy level only contains 8 electrons principal energy levels get closer together as they get further from the nucleus orbitals are always filled in numerical order


Home



The Actinide Research Quarterly 1st Quarter 04



Pin By Fernando Visintin On Science Physical Chemistry Electron Configuration Teaching Chemistry


Parsing Spdf Orbital Hybridization And Simple Bonding


S P D F Orbitals Chemistry Socratic


Figure A 1 Angular Dependence Of The S P D And F Orbitals With L Download Scientific Diagram


An Atomic Model Our Present Model Of The Atom Is Based On The Concept Of Energy Levels For Electrons Within An Atom And On The Mathematical Interpretation Of Detailed Atomic Spectra The Requirements For Our Model Are Each Electron In A Particular Atom


Parsing The Spdf Electron Orbital Model


Parsing Spdf Orbital Hybridization And Simple Bonding



Spdf Orbitals Location Diagram Quizlet


Parsing The Spdf Electron Orbital Model


Q Tbn And9gcq8dvoj3blbzibn Pinxfr5zpqto 2 5yk28pboysmjqllqn0mr Usqp Cau
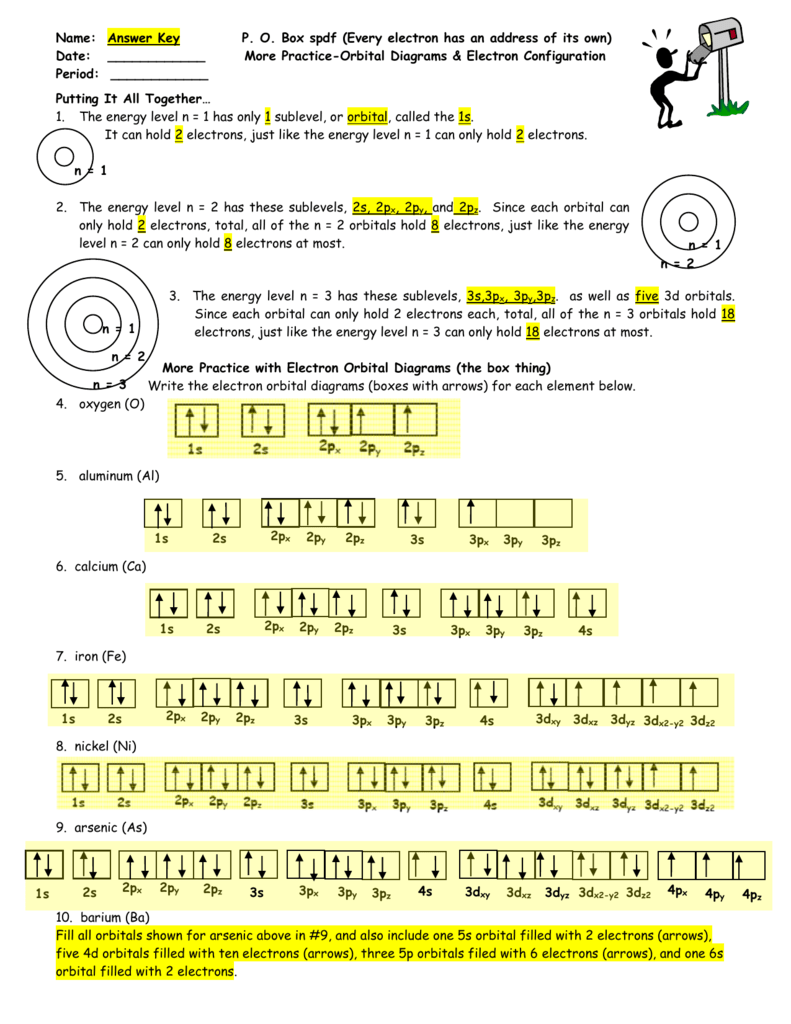


Po Box Spdf Worksheet Answer Key


Atomic Orbitals



Write The Electron Configurations For P And Cl Using Both Sp Clutch Prep



Electron Configuration Wikipedia



Orbitals Lecture Notes 6 Warning Tt Undefined Function 32 Warning Tt Undefined Studocu



Parsing The Spdf Electron Orbital Model Chemistry Education Chemistry Classroom Teaching Chemistry


S P D F Orbitals Chemistry Socratic
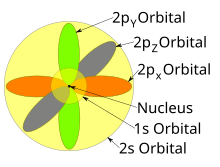


Atomic Orbital Wikipedia


Parsing The Spdf Electron Orbital Model
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/energylevels-56a129545f9b58b7d0bc9f39-5aeb7f1aae9ab800373981a3.png)


S P D F Orbitals And Angular Momentum Quantum Numbers



File Atomic Orbital Clouds Spdf M0 Png Wikimedia Commons



Origin Of Spdf Orbitals Youtube



What Are Orbitals And Its Shapes S P D F Orbitals Shapes Class 9 Class 11 Chemistry Youtube Youtube


Shapes Of Orbitals And Sublevels



The Atomic Spectrum Of Hydrogen Orbitals And Spdf Notation Electromagnetic Spectrum Emission Spectrum
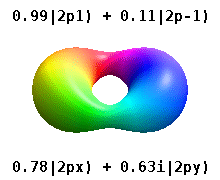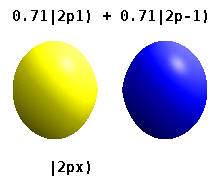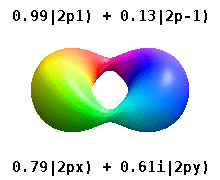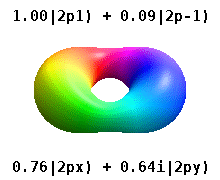


Atomic Orbital Wikipedia
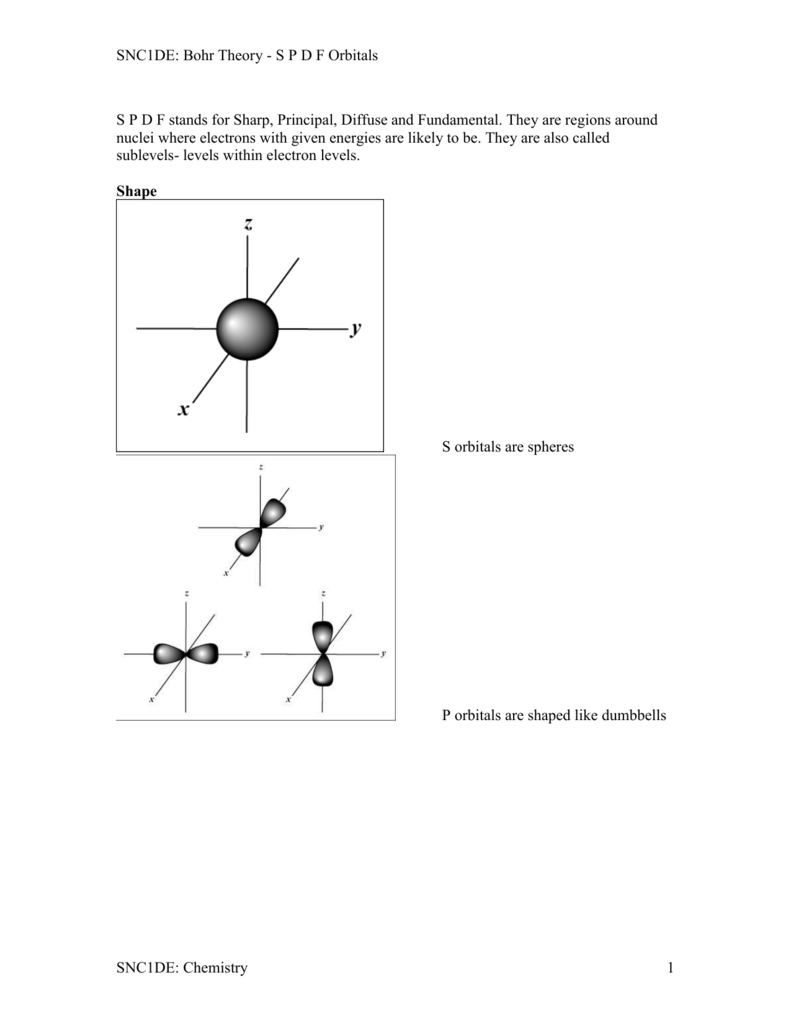


S P D F Orbitals
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/aufbauexample-56a129555f9b58b7d0bc9f48.jpg)


S P D F Orbitals And Angular Momentum Quantum Numbers
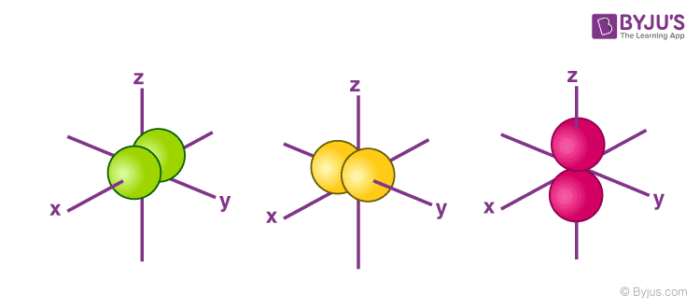


Orbitals Chemistry Shapes Of Atomic Orbitals Shape Of S P D And F Orbital
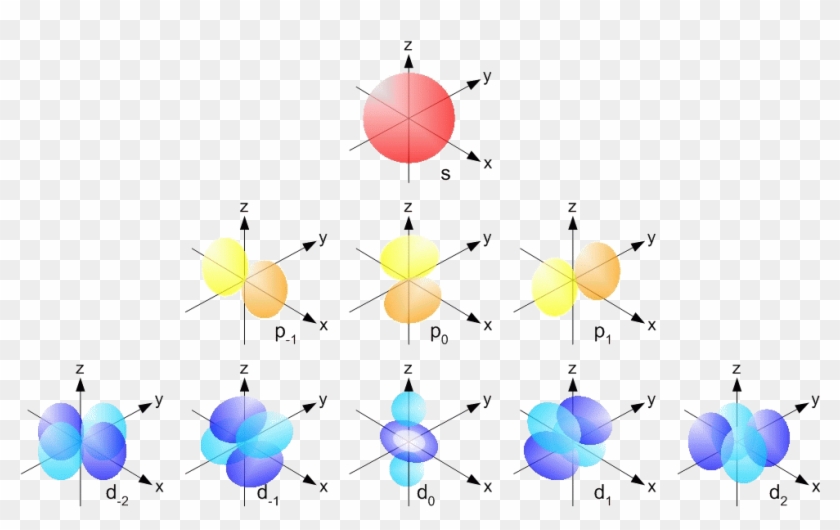


4 Quantum Numbers Of An Electron Orbisophchemistry P And D Orbitals Free Transparent Png Clipart Images Download



Introduction To Electron Configurations Video Khan Academy


Parsing The Spdf Electron Orbital Model Chemistry
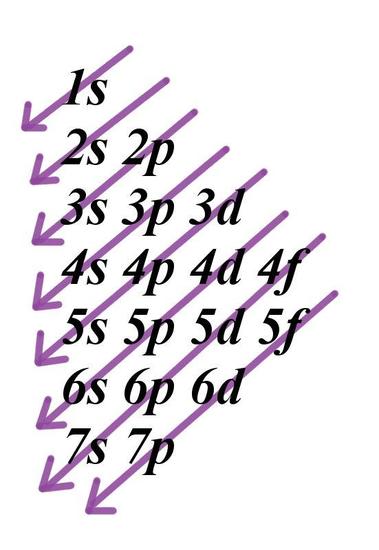


1 4 Electron Configurations Electronic Orbital Diagrams Review Chemistry Libretexts
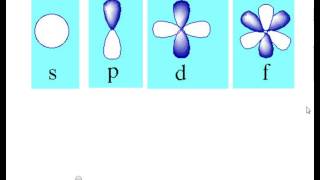


Quantum Model And Spdf Orbitals Youtube



Why Different Orbitals Have Different Shapes Britannica



Atomic Orbitals 5 1 Continued Tutorial Sophia Learning


Electron Configurations



Parsing The Spdf Electron Orbital Model High School Chemistry Teaching Chemistry Chemistry



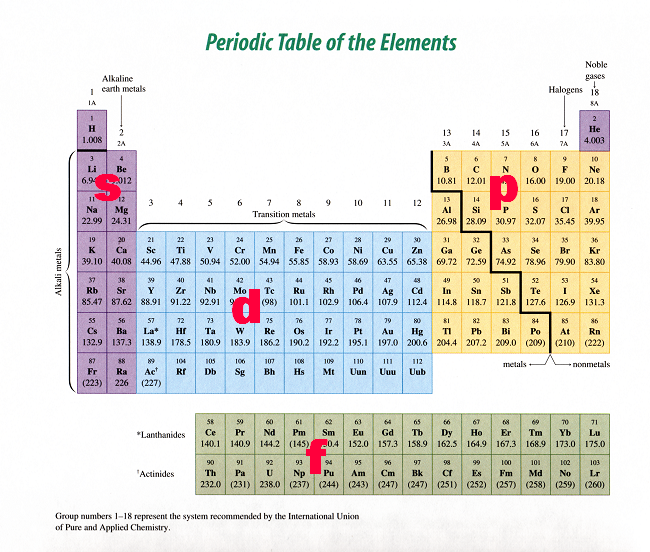
41 The Periodic Table S P D F Blocks Madoverchemistry Com
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/4fz3-electron-orbital-117451436-587f69f23df78c17b6354ebd-f7499851032246f5bbe03f1ffba963d5.jpg)


S P D F Orbitals And Angular Momentum Quantum Numbers


Parsing Spdf Orbital Hybridization And Simple Bonding


Chapter 2 5 Atomic Orbitals And Their Energies Chemistry Libretexts



S P D F Orbitals Explained 4 Quantum Numbers Electron Configuration Orbital Diagrams Youtube



October 13 Ghhs Chemistry


Visualizing Electron Orbitals


Electron Configuration Spdf Notation Part 1 Youtube


Parsing Spdf Orbital Hybridization And Simple Bonding


How Were The Shapes Of S P D And F Orbitals Determined How Did They Get Their Names Of S P D And F Socratic


Shapes Of Orbitals And Sublevels



Unit 4 Topic 1 Spdf Ppt Download


Molecular Structure Atomic Orbitals


Vixra Org Pdf 1308 0130v1 Pdf


Electron Shells And Orbitals Stone Cold Chemistry Talk


Orbitals Atomic Energy Levels Sublevels Explained Basic Introduction To Quantum Numbers Youtube


Shapes Of Orbitals By Science And The Big Ideas Tpt



A Chart Of The Spdf Electron Orbitals Chemistry Education Chemistry Classroom Teaching Chemistry


Spdf Orbitals Can Hold How Many Electrons Qecs Bamagien Site



Orbits And Orbitals Klm Vs Spdf Klm And Spdf Klm Old Style Lettering For The Shells Or Orbits K Is Closest To The Nucleus L Is Next M N O P Ppt


Orbitals The Basics Atomic Orbital Tutorial Probability Shapes Energy Crash Chemistry Academy Youtube


How Many Electrons Can S P D F Orbitals Hold S Bravo Art Back Pain Doctor Delray Beach Utilities


Q Tbn And9gcsijac D7g387kafhktu Pzbpr4ckophzrrfeiqucbkjnqlb H8 Usqp Cau


Parsing Spdf Orbital Hybridization And Simple Bonding



S P D Block Periodic Table Periodic Table Timeline


Parsing Spdf Orbital Hybridization And Simple Bonding



S Sphere P Dumbbell D Clover F Probability Orbitals Ppt Download



Powerpoint Orbital Shape Orientation Spdf Periodic Table Powerpoint Presentation Free Online Download Ppt 6tz333


Orbitals Chemistry Shapes Of Atomic Orbitals Shape Of S P D And F Orbital



The Trouble With The Aufbau Principle Feature Rsc Education


Sublevel Spdf Chart Fgkb Katasekan Site


S P D F Orbitals Chemistry Socratic



コメント
コメントを投稿